It was Shakespeare who wrote, “The evil that men do lives after them; the good is oft interred with their bones.” The Bard was obviously unfamiliar with our brand of Western history, which inverted that truism. Consider the epitaph of famed Texas Ranger Captain Bill McDonald: No man in the wrong can stand up against a fellow that’s in the right and keeps on a-comin’. In a similar vein popular culture tends to paint every Western lawman as a Marshal Matt Dillon, that radio and television paragon of virtue who kept the peace in Dodge City, Kan.
Historian Jay Robert Nash, among others, has debunked the stereotypical image of the Western outlaw-gunman as the sociopathic product of a broken home who despises all authority figures. But few writers have debunked the idealistic stereotype of the Western lawman. Indeed, certain hagiographic historians universally laud them for their courage, dedication to duty and strong family ties. Even Nash refers to such officers “the few good men” who cleaned up the West.
A closer examination reveals a more nuanced view, for many, if not most, officers in the Old West worked both sides of the law, either out of necessity to supplement their meager pay or simply because they were bent that way. It is virtually impossible to name one notable lawman who did not have a few stains on his record. Such men didn’t go through the background checks that are standard today, and their records did not follow them around. Thus, a man could commit bank robbery or murder in New Mexico Territory, yet get hired on as marshal of a small Texas town. Big cities like Dodge did conduct careful searches for their marshals. Regardless, the kind of tough hombre needed to clean up a wild and woolly cow town didn’t figure to be a straight arrow. Just the opposite. The more dangerous reputation a man bore, the more likely he was to be hired for the job. Wild Bill Hickok didn’t earn his reputation with a gun by shooting tin cans.
Nor was it especially difficult to get away with working both sides of the street. The outlaw became a lawman simply by putting on a badge, and the lawman could operate a quiet side business in cattle rustling, extortion or gun-for-hire escapades without anyone being the wiser. The only recognizable difference between them was the badge, and any old body could slap on a tin star and cop an attitude. That became a serious enough concern in Fort Worth that in 1889 the City Council passed an ordinance making it a crime to impersonate an officer. The ordinance is known to have been enforced in only two instances—that fall when a couple of young bravos were fined $10 and $5 respectively in city court for “personating [sic] policemen.”
Lawmen and outlaws had a natural simpatico, derived oftentimes from having been brothers-in-arms in the recent Civil War, or perhaps from having driven longhorns up the Chisholm Trail together. Others were blood relations. Jesse James had no trouble cobbling a gang together from his brother and fellow Confederate bushwhackers after the Civil War. Of course, Jesse never felt moved to put on a badge. He kept to his side of the street. But for so many others the line between good guy and bad guy remained hazy. One wag said the only way to distinguish one from the other after a gunfight was to turn over the corpse and see if it was wearing a badge.
Those who knew such men personally saw past their dime-novel personas. Interviewed in 1931, Kansan Annie Anderson, a former dance hall girl who knew Wyatt Earp, Bat Masterson and pals, insisted, “They were a bunch of cowards.” Though their actions certainly don’t bear out such an assertion, neither were they regarded as upstanding citizens by much of the population.
Men of Action
The familiarity between lawmen and outlaws was also due in part to the fact both groups comprised men of action. Thus, they had a rough, mutual respect for each other—that is, when not shooting at one another. Hired gun and sometime lawman Jim McIntire, for example, was always welcome in the home of Fort Worth Marshal Ed Terrell. Texas Rangers showed similar courtesy to Fort Worth marshal turned gun for hire Jim Courtright in 1884 when arresting him on a murder warrant out of New Mexico Territory. Tarrant County Sheriff Walter Maddox and Fort Worth Marshal Bill Rea treated the jailed fugitive more like an honored guest than a wanted man, thus it’s no surprise Courtright managed to escape with little trouble. When Fort Worth private detective Heck Thomas brought the body of murderer Jim Lee through Gainesville, Texas, in September 1885, he told a reception party admiringly, “He died game, fighting as long as there was breath in his body.” High praise indeed from the man tasked with bringing in the notorious Lee brothers, dead or alive.

(University of Texas Arlington Libraries)
Earlier that year, when U.S. Marshal Harrington Lee “Hal” Gosling was escorting two men to prison, a friend remarked the marshal treated them “more like friends than a brace of the most villainous desperadoes ever consigned to the keeping of an officer.” Gosling’s failure to take routine precautions enabled his prisoners to arm themselves and escape, killing the marshal and two others in the process. A lesson learned the hard way.
Even the worst of outlaws could count friends in law enforcement. An 1892 petition to pardon cold-blooded killer John Wesley Hardin, then serving time at the Texas State Penitentiary in Huntsville, bore the signatures of Tarrant County Sheriff John C. Richardson and former Tarrant County Sheriffs Walter Maddox and Ben Shipp. Ironically, the man Hardin had been convicted of murdering was a deputy sheriff.
Conversely, a hard-boiled outlaw might tip his hat to an honest lawman like Sheriff Tom Bell, of Hill County, Texas. In 1898 convicted murderer John B. Shaw wrote to Bell from his Cleburne death cell:
“Tom, [I knew] if I was caught, you would do it or cause it. It makes me love a man for him to rustle hard. I believe if a man is an officer, he ought to be an officer; if he is a thief, he ought to be a thief. I think more of [Johnson County Sheriff] Bill Stewart for rustling hard for me.”
Shaw signed the note “respectfully” and even invited Bell to come see him before his date with the gallows.
It didn’t hurt a lawman’s reputation to have a few formidable gunfighting friends he could call on if needed. While sheriff of Ford County, Kan., Bat Masterson benefited from his close relationship to the Earp brothers, Doc Holliday and Luke Short, not to mention brother Ed, a Dodge City policeman. The street ran both ways. When Short ran afoul of Dodge City’s powers that be in 1883, he called on Wyatt, Bat and other pals to back his play. They went down in history as the ironically named “Dodge City Peace Commission.”
The fact is some of the most notorious killers in Old West history wore a badge at one time or another. Edward Capehart O’Kelley is remembered today as the man who in Creede, Colo., on June 8, 1892, shotgunned Bob Ford to avenge the latter’s assassination of Jesse James a decade earlier. A certifiable sociopath, O’Kelley—nicknamed “Red” for his hair color and not his bloodthirsty nature—also happened to be a town marshal in nearby Bachelor, Colo.

(Granger)
Another Jekyll-and-Hyde type was Ben Thompson, who drank, gambled and shot his way across Texas before being elected city marshal of Austin in 1880. Wearing a badge did nothing to moderate the marshal’s violent ways, and he spent more time at the gambling tables than patrolling the streets. In 1882 Thompson killed San Antonio saloonman Jack Harris. Though the marshal was acquitted of all charges, Austin’s city fathers forced him to resign. Thompson’s closest pal, rustler-gunslinger King Fisher, also worked the other side of the law as a Uvalde County deputy sheriff. On March 11, 1884, the two were gunned down in Harris’ San Antonio saloon in a revenge killing. The Austin newspaper Texas Siftings recalled Thompson as “the best city marshal in Texas.” Not all his constituents would have agreed.
Henry Newton Brown was another well-known gunman with several notches on his pistol grips when serving as a lawman in Tascosa, Texas, and later as town marshal of Caldwell, Kan. While wearing the badge in Caldwell, he organized a failed bank robbery at Medicine Lodge, Kan., that got him lynched.
The good people of El Paso and the surrounding county had the bad judgment to make sociopathic killer Mannie Clements Jr. a constable and deputy sheriff. On being booted after his acquittal for armed robbery, he was assassinated in a city saloon in 1908.
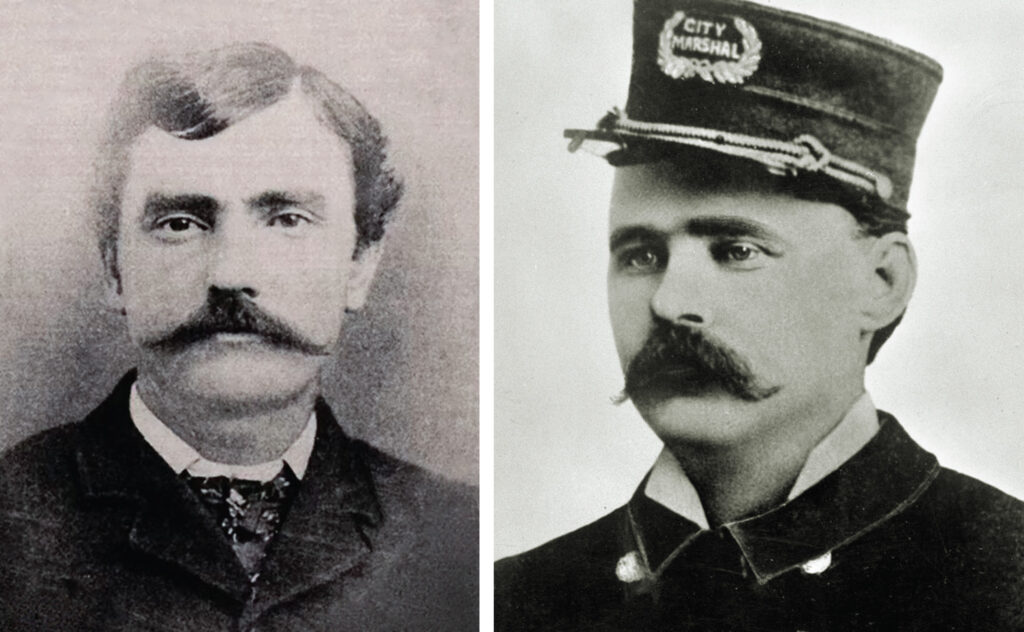

(Left: Philips Collection; Right: Library of Congress)
David Kemp killed his first man in 1879 when he was but 15. Sentenced to hang, he was granted a pardon by the governor of Texas. In 1890 he relocated to Eddy County, New Mexico Territory, where he served as sheriff before killing his successor, Sheriff Les Dow, on Feb. 18, 1897. Found not guilty, Kemp settled into domestic life as a (thrice) married saloonkeeper.
The appropriately named Baz Outlaw was a member of the vaunted Texas Rangers with a predilection for gunplay when he drank too much, which was often. Though the fed-up Rangers ultimately discharged him, Outlaw parlayed his credentials into an appointment as a deputy U.S. marshal. On April 5, 1894, while on a bender in El Paso, he shot and killed a Texas Ranger before being gunned down by Constable John Selman.
Selman himself was no monument to justice. Before being elected constable of El Paso, he’d rustled cattle and terrorized citizens in Shackelford County as a deputy under crooked Sheriff John M. Larn. In addition to killing Outlaw, the corrupt constable back-shot Hardin, killing him, and engaged in repeated drunken quarrels. One such quarrel, with Deputy U.S. Marshal George Scarborough on April 2, 1896, got Selman killed. Despite his checkered career, his headstone bears the simple inscription John Henry Selman… El Paso Constable.
Another El Paso lawman of questionable virtue was Dallas Stoudenmire. Appointed city marshal in 1881, he spent a year doing a commendable job, which included gun battles with a host of ne’er-do-wells. Unfortunately, Stoudenmire too exhibited a weakness for alcohol, which made him belligerent and quarrelsome and led city fathers to fire him. Months later, on Sept. 18, 1882, he died as so many lawman-outlaws did, in a saloon gunfight.
Best known as a gun for hire, “Killin’ Jim” Miller served at various times as a deputy sheriff, town marshal and Texas Ranger. On Sept. 13, 1896, then Pecos Marshal Miller publicly gunned down former county sheriff and longtime nemesis Bud Frazer in a Toyah, Texas, saloon. It says something about Frazer’s reputation that a jury acquitted Miller. Later advertising his services as a paid assassin, Miller offered to kill anyone for $150.
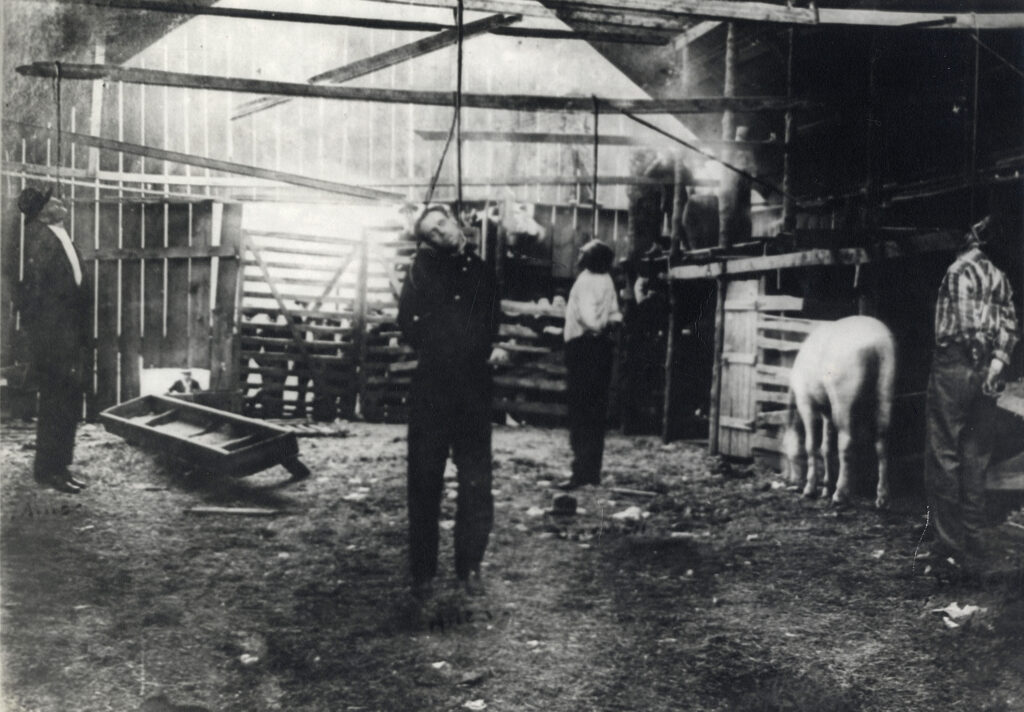

a notorious gun for hire. Among his victims
were a fellow lawman in Pecos, Texas, and a
U.S. marshal. The latter killing earned Miller
(at left) and cohorts this 1909 necktie party.
(McFarlin Library, University of Tulsa)
By his early 30s “Mysterious Dave” Mather had spent much of his young life behind bars in Texas, Kansas and New Mexico Territory. Between jail stints the adept gunhand had no trouble finding work as a lawman. The difference in opinion regarding Mather’s reputation in Dodge City and Dallas, respectively, is mysterious indeed. In 1885 the Dodge City Times hailed him as a “good officer,” while the Dallas Daily Herald deemed him “a notorious horse thief, stage robber and murderer.”
Yet another lawman with a checkered reputation and colorful moniker was Fort Worth’s “Longhair Jim” Courtright, who served three terms as city marshal in the mid- to late 1870s. Depending on one’s perspective, he either tamed the town or tolerated a disgraceful degree of lawlessness. On losing his fourth run for office, he went wholly over to the dark side as a hired gun and extortionist. Courtright, too, died in a shootout, on Feb. 8, 1887—only it was in front of a saloon (Fort Worth’s White Elephant), as the fallen marshal had been gentlemanly enough to call out rival Luke Short for a proper showdown.
A Higher Standard
Not all bad behavior by badge wearers ended in death. On April 3, 1889, Fort Worth officers Jim Rushing and John W. Coker were tying one on in the red-light district known as Hell’s Half Acre when fellow officer Pat Stevens stepped in to arrest the raucous duo. When they resisted, all three men drew their weapons. Stevens fired a shot before terrified onlookers disarmed him, and cooler heads prevailed. It was only dumb luck no one was hit, let alone killed. Initially charged with “assault to murder,” Rushing and Coker were let off with a reprimand. After all, they were officers, and no one had been injured.
Rules governing officers’ behavior came late to Western law enforcement. In 1882 Dodge City Mayor Alonzo B. Webster drew up one of the first such set of rules for a department West of the Mississippi. Borrowed from similar codes back East, it called for officers to be “quiet, civil and orderly” and to maintain “decorum, command of temper, patience and discretion.” A year later the Galveston City Council laid down rules that included this challenge: “Policemen shall not become offended at any harsh or abusive language that may be applied to them, and they will not make arrests in their own quarrels or those of their own families.”

(News Tribune Publishing)
But it took Sam Farmer, who served two stints as Fort Worth marshal (1879–83 and 1887–91), to lay down the law in Texas with regard to using deadly force. Prior to his tenure it was common practice for officers to use whatever force they deemed necessary to do the job. Farmer set a higher standard for his force with 11 rules, including these notable few:
No. 3—Use no more force than absolutely necessary to make an arrest.
No. 4—Never make an arrest merely because someone is saucy toward you.
No. 10—Wear six-shooters out of sight and only use them in self-defense; anything more than that is illegal.
Of course, setting down rules on paper meant nothing if not enforced. And in Fort Worth at least, they must not have been, as the general run of lawmen didn’t noticeably improve after the turn of the century. Things still operated pretty much the same as they had in frontier days. Consider, for example, Captain Tom McClure. For much of his seven years on the force, the captain turned a blind eye to bootlegging and illegal gambling, presumably for a price. Not until 1922 did the police department get wind of things and force McClure into retirement. The city declined to prosecute, likely weighing the public embarrassment certain revelations would have caused.
Passage of both the 1914 Harrison Narcotics Act and the 1919 National Prohibition Act actually spawned new temptations for officers. Recall that many virtually lived in saloons when not on duty—and sometimes while on duty—and more than a few died in gun battles in those same haunts. Others had moonlighted as bouncers or bartenders. It couldn’t have been easy for them to turn their backs on that part of their lives. Likewise, drug dealing had been another way for men forced to make do on the piecework “fees-and-fines” system to supplement their meager income. By 1922 the rumor mill in Fort Worth was rife with reports of “persons in police uniform” peddling illegal whiskey and narcotics. Investigating federal agents found the rumors to be true. The kingpin behind most of the illicit trade turned out to be not some drug lord or bootlegger but a special county policeman.
Sheriff departments also had their share of bad apples. The 1903 year-end report of the Fort Worth Police Department recorded the arrests of four of Tarrant County Sheriff John T. Honea’s deputies on various offenses. None of the cases made it into the newspaper.
The Power of the Dark Side
Trying to delve into the psyches of men who lived a century or more ago is a challenge. What forces drove lawmen to the dark side? Money issues are only part of the equation. Inner demons? Drink? A thirst for power? Entitlement? Some combination of the above? Forensic psychiatrist R. Gregory Lande argues that the dehumanizing effect of the Civil War, particularly the horrors men had witnessed, was the biggest single reason for the postwar crime wave. Such a rationale also explains a related rise in alcoholism and drug use over the same period.
That said, no one answer fits all. The reasons certain high-profile lawmen went bad are less speculative. For instance, Deputy U.S. Marshals Bob and Grat Dalton decided there was more money to be made robbing trains than preserving law and order, while Mather associate Milt Yarberry, Albuquerque’s first town marshal, was simply a vicious bully who preferred a life of crime to living peacefully. On Feb. 9, 1883, after one of his victims showed up dead with a bullet in the back, Yarberry was marched to the gallows.

(Sgt. Kevin Foster, Fort Worth Police Department, Ret. )
Men of Yarberry’s ilk treated the badge as a license to do whatever they pleased, and reform was slow to come. In 1908 Fort Worth mounted officer Hugh Glosson placed his horse in the path of two cars preparing to drag race down Hemphill Street. When their drivers sped past the officer on either side, Glosson yanked and leveled his sidearm at them before ordering the drivers out of their cars. As they were unarmed and had their lady friends with them, the drivers objected to Glosson’s threatening manner and filed a complaint with the police department. At the subsequent hearing Glosson said the cars had scared his horse, and he would only have shot out a tire had the drivers not pulled over. No surprise, the department sided with Glosson, who went on to a long and feisty career in uniform in Fort Worth.
Despite what one reads in today’s headlines, law enforcement has come a long way from the days when a “cowboy culture” prevailed in many departments out West. Professional standards are higher, rules are in place, and the public is less tolerant of official misbehavior. Only when we view Western law enforcement through the nostalgic prism of “the good ol’ days” do we risk buying into the dime-novel version of history.
For further reading on the topic author Richard Selcer recommends Texas Gunslingers, by Bill O’Neal, and Encyclopedia of Western Lawmen & Outlaws, by Jay Robert Nash.